Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakurai, Shinji; Kawashima, Hisato; Higashijima, Satoru; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Masaki, Kei; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shibama, Yusuke; Sakasai, Akira
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.891 - 894, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The entire plasma facing components should be water-cooled in JT-60SA. A cassette module of divertor is introduced for remote maintenance. The divertor targets are mounted on the cassette. A brazed carbon fiber composite target is promising candidate for the divertor target. The latest results of mock-ups test clarified that thermal fatigue life cycles are more than 1000 cycles of 15 MW/m
 10 sec. The divertor is designed to control divertor detachment for heat load reduction. The vertical targets and a "V-shaped corner" like as that in ITER are adopted to enhance detachment. Divertor heat load and pumping efficiency has been evaluated, using 2D plasma fluid (SOLDOR) and neutral Monte-Carlo (NEUT2D) code. The plasma detachment occurs near the outer-strike point within the "V-shaped corner", which results in low peak heat flux density 5.8 MW/m
10 sec. The divertor is designed to control divertor detachment for heat load reduction. The vertical targets and a "V-shaped corner" like as that in ITER are adopted to enhance detachment. Divertor heat load and pumping efficiency has been evaluated, using 2D plasma fluid (SOLDOR) and neutral Monte-Carlo (NEUT2D) code. The plasma detachment occurs near the outer-strike point within the "V-shaped corner", which results in low peak heat flux density 5.8 MW/m for the case with additional gas puff of 5
for the case with additional gas puff of 5 10
10 /s compared to 11.4 MW/m
/s compared to 11.4 MW/m for the case without "V-shaped corner".
for the case without "V-shaped corner".
Nakano, Tomohide; Kubo, Hirotaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Higashijima, Satoru
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.255 - 258, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Therefore it is concluded that the dominant radiator, C , is produced by ionization of C
, is produced by ionization of C and recombination of C
and recombination of C at similar rates around the X-point in the detached plasma, and that C
at similar rates around the X-point in the detached plasma, and that C is the second biggest radiator. Further the transport loss of C
is the second biggest radiator. Further the transport loss of C will be investigated by an impurity transport code (IMPMC), in addition to comparison of the radiation power and atomic processes.
will be investigated by an impurity transport code (IMPMC), in addition to comparison of the radiation power and atomic processes.
Shu, Wataru; Nakamichi, Masaru; Alimov, V.; Luo, G.-N.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.1017 - 1021, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:95.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Ono, Noriyasu*; Tanaka, Hirohiko*; Kawashima, Hisato; Nakano, Tomohide
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.364 - 367, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Characteristics of the fluctuations at three locations (Low-Field-Side midplane, X-point, and High-Field-Side SOLs) of the JT-60U SOL were investigated in L-mode and ELMy H-mode plasmas. Influence of their poloidal asymmetry at the LFS and HFS on the parallel plasma flow was investigated. For the L-mode, poloidal asymmetry in djs/ js
js was enhanced at the LFS midplane (40-60%), while it was small (10-20%) at the HFS SOL and LFS X-point. On the other hand, djs/
was enhanced at the LFS midplane (40-60%), while it was small (10-20%) at the HFS SOL and LFS X-point. On the other hand, djs/ js
js was similar (20-30
was similar (20-30 ) for the ELMy H-mode. Statistical properties (Skewness) and their poloidal asymmetry were different in the ELMy H-mode and L-mode plasmas. In the ELMy H-mode, positive S (= 0.3-0.5) was seen near the separatrix. However, in the L-mode, larger S (=0.5-0.9) was observed at the LFS midplane, and it extended to the far SOL (r
) for the ELMy H-mode. Statistical properties (Skewness) and their poloidal asymmetry were different in the ELMy H-mode and L-mode plasmas. In the ELMy H-mode, positive S (= 0.3-0.5) was seen near the separatrix. However, in the L-mode, larger S (=0.5-0.9) was observed at the LFS midplane, and it extended to the far SOL (r 10 cm). In-out asymmetry in the intermittent transport will contribute to produce the SOL flow pattern.
10 cm). In-out asymmetry in the intermittent transport will contribute to produce the SOL flow pattern.
Itami, Kiyoshi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kaminaga, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.983 - 987, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:70.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In series of experiments in 2000 and 2008, ECRF (Electron Cyclotron Range of Frequency) wall conditioning discharges were extensively studied in JT-60U with toroidal magnetic field of 
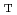 = 3.6 T and ECRF heating power of PECH
= 3.6 T and ECRF heating power of PECH  2.5 MW. Homogeneous He (helium) conditioning discharges were reproducibly obtained by applying the horizontal field as large as 0.2% of
2.5 MW. Homogeneous He (helium) conditioning discharges were reproducibly obtained by applying the horizontal field as large as 0.2% of 
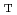 . It was found that the horizontal field is effective to extend He plasma toward high field side from the fundamental ECH resonant surfaces. The ECRF wall conditioning discharge with PECH = 2.5 MW and pulse length of
. It was found that the horizontal field is effective to extend He plasma toward high field side from the fundamental ECH resonant surfaces. The ECRF wall conditioning discharge with PECH = 2.5 MW and pulse length of 
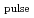 = 1.5 s was applied to the plasma disruption with the stored energy of W = 3.3 MJ. And the successful recovery of the current ramp-up with 0.5 V/m of ohmic electric field was obtained.
= 1.5 s was applied to the plasma disruption with the stored energy of W = 3.3 MJ. And the successful recovery of the current ramp-up with 0.5 V/m of ohmic electric field was obtained.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Nobuta, Yuji*; Hayashi, Takao; Masaki, Kei; Sato, Masayasu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.635 - 638, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.3(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated hydrogen isotopes retention in the outboard first wall tiles of JT-60U by means of TDS, SIMS and SEM. The outboard first wall tiles of JT-60U are mostly eroded. The total retention (H+D) normalized by a unit area and integrated NBI time in the eroded first wall tiles and the eroded divertor tiles were nearly the same, in spite of the lower temperature of the first wall. Differently from divertor tiles, in which H retention was dominated owing to HH discharges preformed after DD discharges, deuterium is dominated in hydrogen isotopes retention and penetrates deeper from the surface. This is attributed to injection of high energy D and difficulty of isotopic replacement owing to their lower temperature. The integrated amount over the whole surface could be appreciably large. This type of hydrogen retention could be also possible for the metallic wall.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; JT-60 Team
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.869 - 875, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Particle control is important for burning plasma control, because fuel density is one of a few controllable parameters in a burning plasma. First, mechanisms responsible for determining density profiles and dependence of impurity transport on density profiles were investigated. Peakedness of density profiles increased with decreasing collisionality, which is consistent with ITG/TEM turbulence theory. However, other hidden parameters, such as toroidal rotation, existed. Metal impurity accumulation was observed with peaked density profile, while light impurity accumulation was not. Next, effects of fuelling on confinement was investigated using newly installed supersonic molecular beam injection (SMBI). SMBI directly affected the plasma parameters at r/a 0.8 as similar as pellet injection. However, confinement degraded with constant pedestal pressure in contrast to pellet injection. Using the burning plasma simulation scheme, it was demonstrated to reduce the simulated a-heating with SMBI due to confinement degradation and flattening of pressure profile.
Nobuta, Yuji*; Arai, Takashi; Yagyu, Junichi; Masaki, Kei; Sato, Masayasu; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Yamauchi, Yuji*; Hino, Tomoaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.643 - 646, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The hydrogen and deuterium retention in gap side surfaces of the first wall tiles exposed to DD and HH discharges in JT-60U were investigated. The hydrogen and deuterium retention and boron deposition increased with the gap width. The depth profile of deuterium was very similar to that of boron, indicating that deuterium was incorporated with boron. Thick carbon deposition layer ( 1e
1e m) was observed in the gap of inboard tile and the atomic ratio in (H+D)/C at the carbon layer was estimated to be approximately 0.15. This value is higher than that observed in the divertor region. In this study, the H+D amount in gap side surfaces of the first wall was of the order of 1e23
m) was observed in the gap of inboard tile and the atomic ratio in (H+D)/C at the carbon layer was estimated to be approximately 0.15. This value is higher than that observed in the divertor region. In this study, the H+D amount in gap side surfaces of the first wall was of the order of 1e23  1e24m
1e24m .
.
Koubiti, M.*; Nakano, Tomohide; Capes, H.*; Ferri, S.*; Godbert-Mouret, L.*; Marandet, Y.*; Rosato, J.*; Stamm, R.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.1142 - 1144, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Hoshino, Kazuo; Toma, Mitsunori*; Furubayashi, Masahiko*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Inai, Kensuke*; Oya, Kaoru*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.168 - 171, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The self-sputtering yield and the reflection yield are important for a prediction of the tungsten impurity content penetrating into the main plasma in future fusion reactors. These yields greatly depend on the incident angle of impurities to the plasma facing components. The IMPGYRO code is applied to the analysis of the angle distribution of incident impurities and the effect of the incident angle and energy on the sputtering and reflection yields. The incident angle distribution is divided into several peaks corresponding to charge states. This is caused by the different acceleration for each charge state by the sheath. In the attached plasma case, the sheath increases the self-sputtering yield. This is due to the change of the incident angle by the sheath rather than the change of the incident energy. On the other hand, in the detached plasma case, the significant effects of the sheath on the sputtering yield and the reflection yield is not seen.
Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kawashima, Hisato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.307 - 310, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The divertor plasma should be cooled significantly by impurities to reduce the heat load onto the divertor plate up to the permissible level in fusion reactor. To achieve enhanced radiation, the control method for impurity retention in the divertor region should be established. Aiming at this impurity control, we have investigated the impurity generation and transport. 2D multi-fluid divertor codes have been developed, where the impurity transport is solved as fluid species. On the other hand, we have developed a impurity transport modelling IMPMC based on Monte-Carlo techniques. The MC approach provides the modelling method to take into account the kinetic effect and the complex dissociation processes of hydrocarbons. Using the IMPMC, the kinetic effect of thermal force on He transport is investigated for JT-60SA detached plasma. Without the recycling process, the kinetic effect of the thermal force is found to increase the He density in the divertor region by a factor of 2, compared with the conventional (fluid) evaluation. However, the kinetic effect is masked by the recycling at the target plates.
Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Shibahara, Takahiro*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Yoshida, Masafumi; Masaki, Kei; Sato, Masayasu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.705 - 708, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tomita, Yukihiro*; Kawamura, Gakushi*; Smirnov, R.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tskhakaya, D.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.164 - 167, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Release conditions of a spherical dust particle from a plasma-facing vertical wall immersed in an oblique magnetic field are studied analytically. The Poisson's equation is solved in the sheath to obtain the electric field at the wall, which repels the dust particle from the wall. The electric field decreases as the direction of the magnetic field approaches parallel to the wall. On the other hand the ion flow velocity becomes larger at moderate oblique angle than that without magnetic field. It is clarified that in the case of the strong magnetic field the critical dust radius for the release of the dust increases as magnetic field becomes more acute. In the case of the weak magnetic field, the critical radius disappears at the moderate angles of the oblique magnetic field.
Hayashi, Takao; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Mayer, M.*; Krieger, K.*; Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Sato, Masayasu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.667 - 670, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Absolute concentrations and the depth profiles of D in plasma-facing graphite tiles used in JT-60U were determined by means of the D( He, p)
He, p) He resonant nuclear reaction. The analyzed samples were not exposed to H discharges before air ventilation. The maximum depth of analysis is about 1.4
He resonant nuclear reaction. The analyzed samples were not exposed to H discharges before air ventilation. The maximum depth of analysis is about 1.4  10
10 carbon (C) atoms/m
carbon (C) atoms/m , corresponding to a linear depth of 16
, corresponding to a linear depth of 16  m for the density of 1.7
m for the density of 1.7  10
10 kg/m
kg/m . The highest D concentration was found at the inboard mid-plane of first wall area. The maximum D concentration is D/C=0.13, and the concentration decrease with the depth. The D retention within 16
. The highest D concentration was found at the inboard mid-plane of first wall area. The maximum D concentration is D/C=0.13, and the concentration decrease with the depth. The D retention within 16  m is 1.9
m is 1.9  10
10 D atoms/m
D atoms/m . The D retentions in this paper were about 2
. The D retentions in this paper were about 2 9 times larger than previous samples, which were located on the same area and exposed to the hydrogen discharges. This indicates the H plasma discharges were effective to remove the D (and T) from graphite tiles in the first wall area.
9 times larger than previous samples, which were located on the same area and exposed to the hydrogen discharges. This indicates the H plasma discharges were effective to remove the D (and T) from graphite tiles in the first wall area.